What Is Acne?
Acne is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. It often causes whiteheads, blackheads, or pimples, and usually appears on the face, forehead, chest, upper back, and shoulders. Acne is most common among teenagers, but it affects people of all ages.
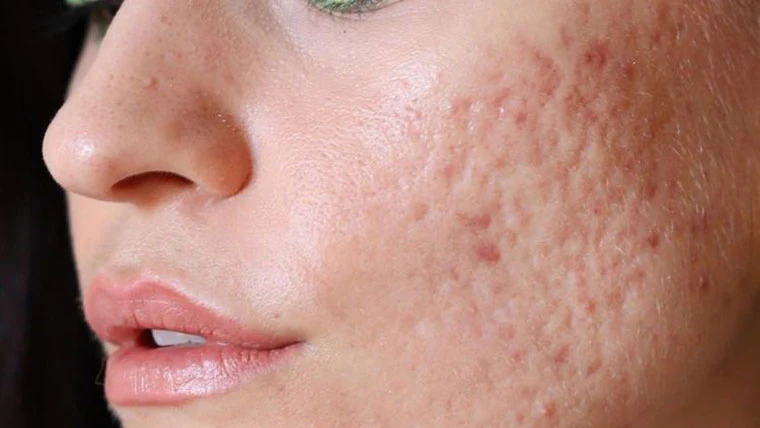
Types of Acne
There are several types of acne, including:
- Whiteheads: Closed clogged pores.
- Blackheads: Open clogged pores.
- Papules: Small red, tender bumps.
- Pustules: Pimples with pus at the tips.
- Nodules: Large, painful lumps beneath the skin.
- Cystic Lesions: Painful, pus-filled lumps beneath the surface.
What Causes Acne?
Acne develops due to a combination of factors:
- Excess Oil Production: Overactive sebaceous glands can clog pores.
- Dead Skin Cells: Accumulation can block hair follicles.
- Bacteria: Propionibacterium acnes can multiply and cause inflammation.
- Hormonal Changes: Especially during puberty, menstruation, or stress.
- Certain Foods: Dairy and high-glycemic foods might trigger breakouts.
- Medications: Drugs like corticosteroids or lithium can worsen acne.
- Cosmetics: Some oil-based makeup and skincare products can clog pores.
Who Gets Acne?
- Teenagers: Due to hormonal shifts during puberty.
- Adults: Adult acne is common, especially among women.
- Genetics: If your parents had acne, you’re more likely to develop it too.
- Stressful Lifestyles: Can worsen existing acne.
- Environmental Factors: Humidity and pollution may contribute.
How to Treat Acne
There’s no one-size-fits-all cure for acne, but several effective treatments can help:
1. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments
- Benzoyl Peroxide: Kills acne-causing bacteria.
- Salicylic Acid: Helps exfoliate and unclog pores.
- Retinoids: Promote cell turnover and prevent plugging.
- Sulfur-Based Creams: Absorb excess oil and dry out pimples.
2. Prescription Medications
- Topical Retinoids (e.g., tretinoin)
- Antibiotic Creams or Pills
- Hormonal Treatments: Birth control pills or anti-androgens.
- Isotretinoin: A powerful oral medication for severe cases.
3. Professional Procedures
- Chemical Peels
- Laser Therapy
- Drainage and Extraction
- Steroid Injections
🔔 Always consult a dermatologist before starting any medical treatment.
Natural Home Remedies for Acne
While natural remedies may not work for everyone, they can help reduce mild acne:
- Tea Tree Oil: Natural antibacterial properties.
- Aloe Vera: Soothes and heals the skin.
- Honey and Cinnamon Mask: Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial.
- Green Tea Extracts: Can reduce oil and inflammation.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: May balance skin pH and kill bacteria.
How to Prevent Acne
- Wash Your Face Twice a Day
Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser. - Avoid Touching Your Face
Your hands carry bacteria and dirt. - Use Oil-Free Makeup and Skincare
Choose products labeled non-comedogenic. - Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water to flush out toxins. - Eat a Balanced Diet
Avoid sugar and greasy foods; eat more vegetables and omega-3 rich foods. - Manage Stress
Practice yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises. - Change Pillowcases Frequently
Dirty fabric can transfer oil and bacteria to your skin.
When to See a Dermatologist
If your acne is:
- Severe or painful
- Not responding to OTC treatments
- Causing emotional distress or scarring
… then it’s time to see a skin specialist.
Final Thoughts
Acne may be frustrating, but with the right skincare routine and treatment plan, it can be managed or even eliminated. Whether you’re dealing with occasional breakouts or severe cystic acne, consistency and patience are key. Don’t give up—clear skin is possible!





